Teams
Team 1: Cloud 1
Project objective
To investigate and compare commercially viable and available cloud computing options.
Scope of project
- Initial ideal market
- Ease of use
- Skills and infrastructure needed
- Cost comparisons
- Risks and cost-benefits
- Conditions for market growth
| Item | Date |
|---|---|
| Project proposal | 9/24/2008 |
| User requirements | 10/1/2008 |
| Survey of market demand | 10/8/2008 |
| Survey of market supply (current products) | 10/15/2008 |
| Upcoming technologies | 10/22/2008 |
| Cost-benefits analysis | 10/29/2008 |
| Risk estimation | 11/5/2008 |
| Risk estimation | 11/12/2008 |
| Skills and infrastructure required | 11/19/2008 |
| Market evolution analysis | 11/26/2008 |
| Draft report | 12/3/2008 |
| Final report | 12/10/2008 |
Team 2: Cloud 2
Project Objective
A competitive analysis of commercially viable cloud computing options
Comparative analysis against traditional application hosting
Project Scope
Our team will focus on the top 5 commercially available cloud computing solutions
We will focus on cost, ease of use, and future growth potential
We will examine options for small, medium and large size companies looking to utilize cloud computing
Our comparative analysis will be limited to a couple traditional application hosting models
Project Deliverables
PowerPoint presentation
Relevant appendices
| Due Date | Interim Deliverable | Format |
|---|---|---|
| Week 1 | Project Scope and Objectives | PowerPoint |
| Week 2 | Identify Target Companies and Supporting Materials | bSpace |
| Week 3 | Identify Target Companies and Supporting Materials | bSpace |
| Week 4 | Cost Structures | bSpace |
| Week 5 | Identify Traditional Application Hosting Comparisons | bSpace |
| Week 6 | Comparative Analysis | bSpace |
| Week 7 | Future Projections | bSpace |
| Week 8 | First Draft of Final Deliverable | PowerPoint |
| Week 9 | Rough Draft of Final Deliverable | PowerPoint |
| Week 10 | Final Project Deliverable | PowerPoint |
Team 3: CVC
Our understanding of the client’s situation:
Meltwater was founded in Oslo, Norway, in 2001 as a provider of software solutions to small and medium enterprises (SMEs). In the last 7 years, the company has introduced 2 successful services in the market based on proprietary technologies:
i) Meltwater News: operations in the electronic media monitoring offered through a search platform;
ii) Meltwater Drive: operations in the software-as-a-service (SAAS) or cloud computing industry, offering mobile access and back-up services.
Meltwater sells and distributes its products and services through a vast and decentralized sales and distribution organization reaching our more than 13,000 clients globally. Such sales and distribution expertise and assets define the company’s core competency.
Going forward, Meltwater wants to leverage on such core competency and develop and acquire new products and services to be sold and distributed through their existing channels. In order to achieve that, the company is considering the creation of a new and separate division in the format of a search fund, to originate and acquire new products and services for the group in the SAAS segment.
Project objective:
The objective is to propose a tactical (executable) business plan for the new division of the group to assess and acquire two new businesses in the SAAS segment by the end of 2009. Such business plan shall allow Meltwater to measure and evaluate performance, and ensure that the division achieves its objectives and adds new businesses and related-products/services to the group.
Schedule and deliverables:
Deliverable / Due date
Benchmark results on modus operandi and structure of existing search funds + corporate venture initiatives / Oct 8th
Preliminary findings on individual remuneration and performance evaluation system / Oct 15th
Deliverable 1: Individual remuneration and performance evaluation system / Oct 22nd
Preliminary findings on investment evaluation methodology / Oct 29th
Deliverable 2: Recommended investment screening and evaluation process / Nov 5th
Preliminary operational model (budget) / Nov 12th
Deliverable 3: Recommended operational model (budget) / Nov 19th
Preliminary findings on legal and organizational structure / Nov 26th
Legal and organizational structure / Dec 3rd
Final deliverable: Final report and budget (MS PowerPoint + MS Excel files) / Dec 10th
Team 4: SAAS 1
Project Goal:
Identify and offer strategic recommendations for new SaaS business opportunities for Meltwater that leverages the company’s current distribution channel and customer base.
Project Scope:
Limit scope to Business to Business SaaS offerings.
Focus on SaaS offerings that have a Global market reach.
Limit SaaS opportunities to targets that require an initial investment of less than $25 mil.
Only consider strategic options that make sense for Meltwater’s current distribution network.
Weekly Goals
Week of:
Sept 22nd: Meet in person with company representatives to determine their exact goals for the project.
Oct 6th: Present a preliminary overview of the Business to Business SaaS market.
Oct 13th: Choose a business functional area segment for further SaaS market analysis.
Oct 20th: Create a list of competitors and products currently in the targeted segment.
Oct 27th: Create a list of possible SaaS offerings that are congruent with Meltwater’s goals and competitive advantages.
Nov 3rd: Deliver a preliminary report with a list of high probability strategic offerings.
Nov 10th : Present final recommendation for new business.
Nov 17th: Deliver rough draft of presentation/report.
Nov 24th: Deliver final draft of presentation/report.
Dec 1st :Present to Meltwater.
Team 5: BBC
Background
The BBC is looking to specify a Digital Terrestrial-based set-top box, based on the
existing "Freeview(tm) box" DTT receiver concept, with an internet connection. The idea
is that the BBC writes the specification and hardware manufacturers build boxes that
conform to the standard, possibly earning a "kitemark" from the "Freeview consortium"
(a group led by the BBC and including other UK broadcasters). Although media
companies and consumer electronics manufacturers are working on internet-enabled
media devices, the difference with the Freeview-sponsored product would be that it is an
industry-wide standard (at least within the UK) and that broadcasters would provide
suitable content before launch, avoiding the "chicken and egg" problem inherent in
hardware standards and specifications.
As part of the set-top box specification, the BBC intends to create a platform for third
parties to create "widgets" or mini-applications that run on televisions. Examples might
be weather forecasts, stock pricing services, currency conversion tools, TV and radio
recommendation engines, news readers, and games.
Approach
- Look at existing technologies - Freeview so far. Review what has worked and what hasn't
- What is the actual business model? Do people buy applications / widgets for their TV, do broadcasters "revenue share" advertising money with the application developers based on usage, or another model?
- Look at other platforms with business models - iPhone, Facebook, others?
- Could this platform work in other countries apart from the UK? Look at China, Spain, Australia, USA — look at government influence, public service vs private, business models, payment models in different countries. Should this platform be created with international usage in mind from the beginning, or should the BBC look to expand into other markets in the future?
- Look at other companies - content, cable, satellite, consumer electronics etc — what are they doing at this time? Who are the big players? What does the value chain look like? Does the value chain differ across the globe?
- Investigate how applications/widgets fit in the value chain. Can application development be globalized? For example, Scrabulous, one of the most popular Facebook apps till recently, was developed by two brothers in India.
- Investigate (and interview?) Silicon Valley companies that have built applications for Facebook, iPhone etc - what would it take for them to build for this platform?
- Investigate how venture capital firms might be involved with such a platform and what it would take for them to be interested (with the Kleiner Perkins "iFund" as the primary example)
- What does BBC get out of creating such a platform? just more viewers, market share, revenue (within the constraints of the BBC's operating model), something else?
- How closely does the BBC (or the Freeview consortium) need to monitor and shepherd the platform specification? Should it provide approvals processes, and provide a "walled garden" of approved applications? Or should it be an open process where TV viewers can add apps themselves? Or a mix of the two?
Report deliverables
- Recommend an appropriate business model, show pros and cons, risks and opportunities (with justification based on the above research on comparable technology platforms)
- Provide overviews of a few startups who would provide applications for such a platform. Summarise what they like about the proposed platform, how such a platform could provide for their needs, what they see as risks and opportunities
- Provide recommendations on the international focus of the model and the platform, including launch strategy and potential international partners
- Provide recommendations on the possibility of venture capital involvement, and how it might work
- Document describing the above, plus a presentation describing the recommendations in Powerpoint format
Timeline
24 September (week 5) - deliver project overview and structure
1 October (week 6) - receive and study information from the BBC describing the project
and work done so far. Overview of the BBC's operations and operating model.
8 October (week 7) - Identify example platforms to be studied. Identify startups to be
investigated
15 October (week 8) - Initial overview of platforms, pros and cons, success criteria and
failure modes
22 October (week 9) - Interview startups who provide applications for comparable
platforms (Facebook apps, iPhone apps etc)
29 October (week 10) - Investigate venture capital involvement, using KPCB's iFund as
an example / case study
5 November (week 11) - Assimilate research
12 November (week 12) - Draft of report and presentation
19 November (week 13) - Second draft of report and presentation
26 November (week 14) - (thanksgiving week, do we have class?)
3 December (week 15) - deliver final report and presentation
10 December (week 16) - (? is there a class this week?)
Team 6: SAAS 2
TEAM 6 - PROJECT PLAN FOR A NEW MELTWATER PRODUCT
INTRODUCTION
Meltwater's current businesses include an electronic clippings service and a web-based content management system. These services are offered in a global, networked setting. In looking at the development of a new venture, we should consider leveraging its existing assets, as follows:
(1) a global salesforce. This salesforce has established trust with customers. This trust will be useful in persuading established customers to try new services. It also provides local knowledge that may be useful in offering services in a globally networked environment.
(2) A global clientel. We don't know much at all about Meltwater's customers. Knowing the size and types of businesses that they cater to will help determine strategy in launching new products.
(3) Lots of data about their clientel. This data store may be valuable in, for example, creating matchups between geographically remote businesses.
(4) Some technical capability.
(5) existing networked computing resources.
These features-a global network and clientele, and an existing networked service-do point to software as a service (SaaS) as a logical direction to take, and Meltwater's newest venture, an enterprise content management system (EMCS), is a first step in this direction. However, the core feature of Meltwater's business is its salesforce, which is globally dispersed and consists of young, motivated, college educated generalists. Through their established customer relationships, Meltwater's salespeople provide a level of trust for their customers that is central to marketing their EMCS product. The amount of research required to put together an enterprise cms system on ones own is considerable, so the idea of going to a trusted source-meltwater-has great appeal. This trust factor may be central in migrating Meltwater's customer base to the "next" product.
PROJECT OBJECTIVE
Identify and analyze new business potential in SaaS for Meltwater that utilizes existing global sale force, global clients and technical capabilities. This might be effected through acquisition or partnering.
PROJECT SCOPE
- Focus on new products that leverage Meltwater's existing sales strategy.
- Focus on global customer base.
- Focus on a strategic growth plan for Meltwater—for movement up the value chain
- Business-to-business sales.
TIMETABLE
Interim Weekly Objectives and Deliverables assuming a Weekly 1/2 Hour Status Update Meeting
- 10/01/08 - Submit revised Project Plan
- 10/08/08 - Identify existing companies in SaaS & the possible market segments (eg. HR, supply chain, procurement, finance, etc.) they fit in
- 10/15/08 - Industry analysis of SaaS
- 10/22/08 - Analyze Meltwater competitive advantages
- 10/29/08 - Develop a set of options for new Meltwater products
- 11/05/08 - Select the best option
- 11/12/08 - Develop a strategic plan for implementing the product
- 11/19/08 - Draft presentation
- 11/26/08 - Final presentation
Weekly Deliverable of 10/08/08
At this preliminary stage, we looked at 23 companies that offer talent management as SaaS. Most of these companies are based in the US. Three companies, StepStone, SyncForce and Caliber, operate primarily in Europe. One is in South Africa. InfoHRM operates in Asia. This sampling of companies have a range of focuses within talent management, such as resume management, workforce planning, job search, performance analysis, market analysis, employee evaluations, workforce planning, or cost of recruitment. Some focus on specific industries or growth companies. Target small, medium, and large companies, and also individuals. Most but not all companies are private and have revenue ranging from about $1M to $144M. Most do more than talent management, offering a range of business services; e.g. marketing management, database management, market surveys, etc.
Weekly Deliverable of 10/17/08
What is Talent Management?
As an online enterprise, Talent Management SaaS is somewhat nebulous. While its core activities include recruiting, tracking, performance management,and development, different online talent management services often provide only a subset of these, or expand the domain to include a broader set of human resources functions. In looking at 23 online talent management software services, we found a great deal of variation in the range of services provided. In the accompanying list, we have broken down the services offered by each company according to a standardized set of categories that represents roughly the full set of services that fall under the rubric of talent management. Different service providers also have different customer bases, including HR departments in firms, employment agencies, and individual job seekers. Since workflows are complicated, these categories inevitably overlap. Also, depending on the customer using the service, the categories may apply in different ways or not at all. CRM, for example, is different depending on whether the customer is a company, agency, or individual. Here are the categories of Talent Management service we have identified:
Recruiting. This includes such activities as collaboration with recruiters, requisition management, source tracking, applicant screening, resume parsing, managing steps in the recruiting process, and job board posting.
Applicant Tracking. Resume creation and filing, applicant status. Candidate management: Creation of candidate profiles, accessing candidates by profile attributes.
Sourcing & Customer Relations Management (CRM). Management of relations with outside agencies and online job posting services, as well as with candidates.
Skills Assessment. Skills tests, interview feedback, background check.
Hiring. Also called “onboarding.” Includes management of tasks involved in the hiring process, forms, documents, provisioning, employee socialization.
Employee Data Management. Benefits, personal time off, etc.
Performance Management. Performance tracking, review and appraisal.
Payroll,Compensation. Timecards, timesheet approval.
Development & Succession. Career goalsetting and development. Training. Succession strategy.
Job Management. Tracking of jobs, projecting of employment needs.
Workforce Planning. Business intelligence, analysis, forcasting, reporting of workforce status (compensation, skill sets, performance, etc) with respect to benchmarks and trends.
Compliance. Functionality designed to ensure that employment/HR program complies with Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO), Office of Federal Contract Compliance Programs (OFCCP), etc
Termination. Provides workflow and documentation for terminating employees (commonly called “offboarding”.
Team 7: Panasonic
Project Objective
To develop a business marketing plan to increase sales of Panasonic's IP cameras
Scope
Examine Panasonic's web-enabled consumer electronics division in the U.S.
Suggest alternative uses for IP cameras
Identify consumers and markets segments
Third-party application development
We will suggest alternative uses and identify new markets for Panasonic's IP cameras. For the most promising ideas, we will investigate the market size, who the customers are, and whether there are other substitutional goods. We will also suggest effective ways to advertise and increase consumer appeal through third-party application development contests. Lastly, we will provide estimated revenue numbers for each of the new product uses. The final deliverable with be a written document and presentation slides of our recommendations.
Weekly Deliverables
| Due Date | Interim Deliverable |
|---|---|
| Week 1 | Project Scope and Objectives |
| Week 2 | Alternative Uses for IP Camera |
| Week 3 | Understand Market for Alternative Uses (size, customers, segmentation, competitors, substitutions) |
| Week 4 | Understand Market for Alternative Uses |
| Week 5 | Advertising & Marketing (positioning of product, distribution channels) |
| Week 6 | Application Development (topcoder.com) |
| Week 7 | Financial Analysis/Revenue Projections |
| Week 8 | First Draft |
| Week 9 | Second Draft |
| Week 10 | Final Project Deliverable |
Team 8: Clean Tech
Project Objective
Identify “clean tech” business opportunities for Panasonic in the US.
Deliverable
Final presentation and supporting written materials recommending specific clean tech business opportunities that Panasonic may exploit in the US. The recommendation will be developed matching the company’s strategy, strengths and capabilities with an analysis of the clean tech market in the United States.
If several opportunities are identified in this study, they will be ranked according to financial factors (market size, profit prospects) and strategic considerations (IPR landscape, number and competitiveness of players, barriers of entry, fit with Panasonic’s strategic plans).
Interim Deliverables
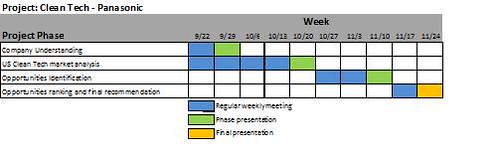
This project will be divided in four phases: 1) Company understanding; 2) US Clean Tech market analysis; 3) Opportunities identification; 4) Opportunities ranking and final recommendation. Each phase will end with a brief presentation in order to discuss progress and collect feedback. Phase 4 will end with final presentation.
Meetings
The team will meet every Tuesday from 12:30 to 2:00pm to consolidate the work performed by members / sub-teams and discuss progress. If a customer representative is available, the team will meet with him / her every Wednesday from 1:20pm to 2:00pm to discuss project development, refine planning and outline goals for the week ahead.
A draft Gantt chart for this project is shown below. This chart is subject to approval from the customer and the course professor. Please note that Phase 1 (Company Understanding) and Phase 2 (US Clean Tech market analysis) will run in parallel during a few weeks. This will be achieved by dividing the team into two sub-teams each focusing in one specific phase. The objective of this division is to assign more time and effort to the second phase, which in our opinion is the most resource-consuming task in this project.
Team 9: Cloud 3
Team Objective
Analyze and comprehensively understand the Cloud Computing sector and to utilize these analysis and presentation techniques in our future careers.
Project Background
Meltwater have a competitive business model in providing online media newsfeeds to numerous corporations based on the cloud computing concept. They now intend to further this business model in other areas; one promising division is referred to by Meltwater as “M Drive”. This sub-division of Melt Water is investigating the business concept of allowing small to medium sized companies to utilize a cloud infrastructure for their IT needs rather than locally manage and maintain their own hardware.
Project Scope
Team 9 will look to conduct a cost-benefit analysis of the Traditional Data Center (TDC) model against the Cloud Computing (CC) model. Areas to be analyzed will include:
- Skills and Investment required in both models
- Options available in each model such as only Data Centre (DC), Managed DC, Managed Application or Hosting
- Cost comparison of the two models for different types of companies (startup, mid size or large)
- Cost of maintenance of the two models (requirements for monitoring, alerts and tools)
Resources required
Team 9 will require from time to time access to Meltwater resources and/or employees; we will make every effort to ensure that this requirement is minimized where possible. A regular 15-30 minute weekly meeting with Professor Wu may be required in order to act as a status check to ensure continual feedback is received on project deliverables.
Project Deliverables
The analysis will result in a 16 page business report that will be delivered by the end of the semester or a date set by Professor Wu. A PowerPoint presentation will also be delivered which will highlight and summarize the report.
Weekly Objectives and Deliverables
| Deliverable | Week |
|---|---|
| High Level Project Summary | 1 |
| Research of Cloud Computing Firms | 2 |
| Research of Traditional Data Centres | 3 |
| Primary Research of Top Players in both | 4 |
| Financial Analysis | 5 |
| First Draft of Final Deliverable | 6 |
| Second Draft of Final Deliverable | 7 |
| Third Draft of Final Deliverable | 8 |
| Fourth Draft of Final Deliverable | 9 |
| No Deliverable this week | 10 |
| Final Deliverable | 11 |
Team 10: Ghana
Project Objectives
To design a 5-year business plan for the business incubator of Meltwater Entrepreneurial School of Technology (MEST) in Ghana.
Basic premises:
MEST incubator will help MEST students to transform their entrepreneurial ideas into entrepreneurial ventures, providing them with business consulting, shared facilities, access to capital and contacts (historically, 87% of worldwide incubator graduates stay in business)
The incubator should yield enough revenues to make MEST self sustainable and be scalable.
Scope of Project
An assessment and recommendation of the right incubator business model and corresponding financial aspects for the next 5 years will be delivered. The BP will include the following sections:
- MEST incubator overview
- Incubators analysis
- Market clusters analysis
- Financial Summary
- Capitalization Requirements
- Strategy and Implementation
Considerations
Successful and failed technology business incubators in US and Europe (e.g. Idealab, Garage) would be studied to find drivers of success and threats
While other potential sources of income and strategies for financial sustainability for MEST might be recommended, the basic focus will be on exploring incubators
Weekly Objectives and Deliverables
| Deliverable | Week |
|---|---|
| Understanding MEST and defining scope | 1 |
| Analysis of Tech Incubators - US | 2 |
| Analysis of Tech Incubators - Europe | 3 |
| Ghana business environment | 4 |
| Potential markets cluster | 5 |
| Definition of MEST incubator model | 6 |
| Financial Analysis - necessities | 7 |
| Financial Analysis - revenues | 8 |
| Financial Analysis - revenues | 9 |
| Final analysis and conclusions | 10 |
| Final analysis and conclusions | 11 |









